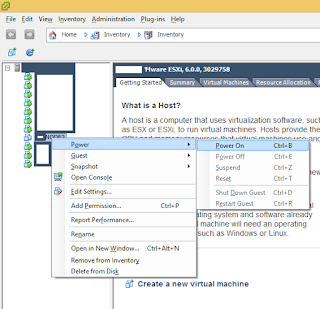
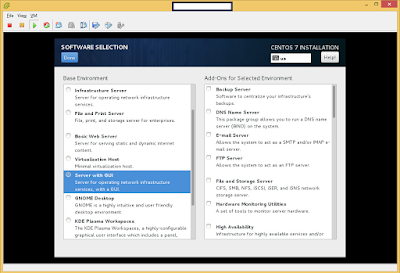
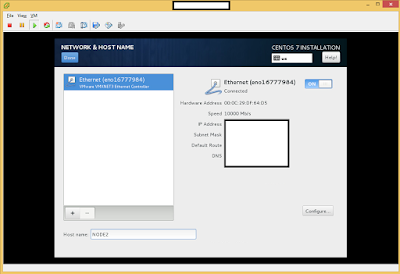
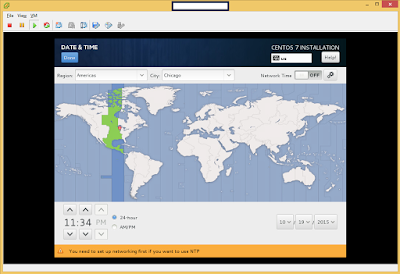
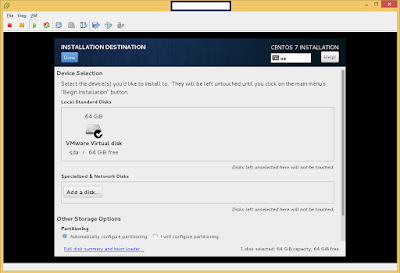
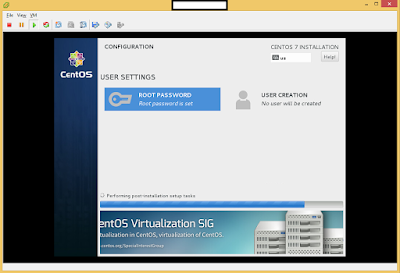
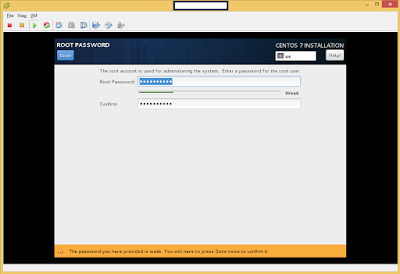
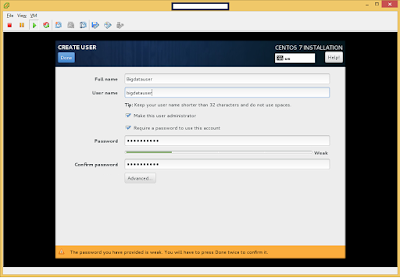
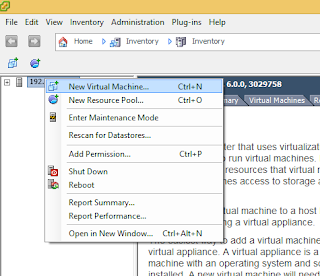
The following is the process of submitting an Apache Storm 0.10 Job.
1. Build your project or projects to a single jar in your local development environment. Refer How to build an Apache Storm 0.10 topology job in Eclipse using Maven?
2. Make sure that you have absolute paths for the configuration files. The preference would be to use Hadoop dfs so that the configuration file can be read by any worker "Supervisor" node. If you can't build with a path is common to all the users i.e under /var/local/storm/ . Do not put this under the user directory like /home/username or /Users/username
3. Make sure the file spout uses absolute path that is common to all users as discussed in step 2.
4. Copy the jar along with the supporting files for config and data files to the Storm master "Nimbus" node.
5. If you do not have Hadoop dfs, then you need to copy the config files and supporting data files to the common location, a common location would be
/var/local/storm/config - for config files
/var/local/storm/topology/topologyname/files and jars
IMPORTANT: you need to copy the supporting files not the jars to all the worker (Supervisor) nodes in the same path. The master (Nimbus) would not copy the supporting files to the worker nodes.
6. Make sure that storm is configured in your path so that you can execute storm command.
7. You can submit a storm job for any other user than the storm cluster is currently running. The only requirement is that the files that you specify should be readable from all the worker nodes in relative paths as well as the storm while submitting the job.
8. Execute the following command from a terminal by first changing directory to the folder that has the jar.
IMPORTANT:
The best practice is to have the first parameter as either local or server to switch execution from a local storm cluster or a production storm cluster.
Do not put a quote or a dash (-) in the command for the jar or the main class name. This is not the same as the java -jar "jarpath" command.
You have to put quotes for all the parameters (arguments) that go into the main class.
9. Go to the Storm UI and check if your job has been submitted and track its status.
http://yourmaster(nimbus)node:8080/
1. Build your project or projects to a single jar in your local development environment. Refer How to build an Apache Storm 0.10 topology job in Eclipse using Maven?
2. Make sure that you have absolute paths for the configuration files. The preference would be to use Hadoop dfs so that the configuration file can be read by any worker "Supervisor" node. If you can't build with a path is common to all the users i.e under /var/local/storm/ . Do not put this under the user directory like /home/username or /Users/username
3. Make sure the file spout uses absolute path that is common to all users as discussed in step 2.
4. Copy the jar along with the supporting files for config and data files to the Storm master "Nimbus" node.
5. If you do not have Hadoop dfs, then you need to copy the config files and supporting data files to the common location, a common location would be
/var/local/storm/config - for config files
/var/local/storm/topology/topologyname/files and jars
IMPORTANT: you need to copy the supporting files not the jars to all the worker (Supervisor) nodes in the same path. The master (Nimbus) would not copy the supporting files to the worker nodes.
6. Make sure that storm is configured in your path so that you can execute storm command.
7. You can submit a storm job for any other user than the storm cluster is currently running. The only requirement is that the files that you specify should be readable from all the worker nodes in relative paths as well as the storm while submitting the job.
8. Execute the following command from a terminal by first changing directory to the folder that has the jar.
storm jar yourproject-1.0.0-jar-with-dependencies.jar com.yourcompany.yourproduct.yourproject.App "server" "/var/local/storm/config/config.json" "/var/local/storm/topology/yourtopology/topologydatafile.json"
IMPORTANT:
The best practice is to have the first parameter as either local or server to switch execution from a local storm cluster or a production storm cluster.
Do not put a quote or a dash (-) in the command for the jar or the main class name. This is not the same as the java -jar "jarpath" command.
You have to put quotes for all the parameters (arguments) that go into the main class.
9. Go to the Storm UI and check if your job has been submitted and track its status.
http://yourmaster(nimbus)node:8080/